What Do They Do?
With so many Jeti telemetry sensors available, it can be quite overwhelming, especially if you are a new Jeti user, to know what might be beneficial to you. We decided that we could make that task less daunting by compiling the most recent list of Jeti sensors and briefly explaining what each one does. Follow along below.
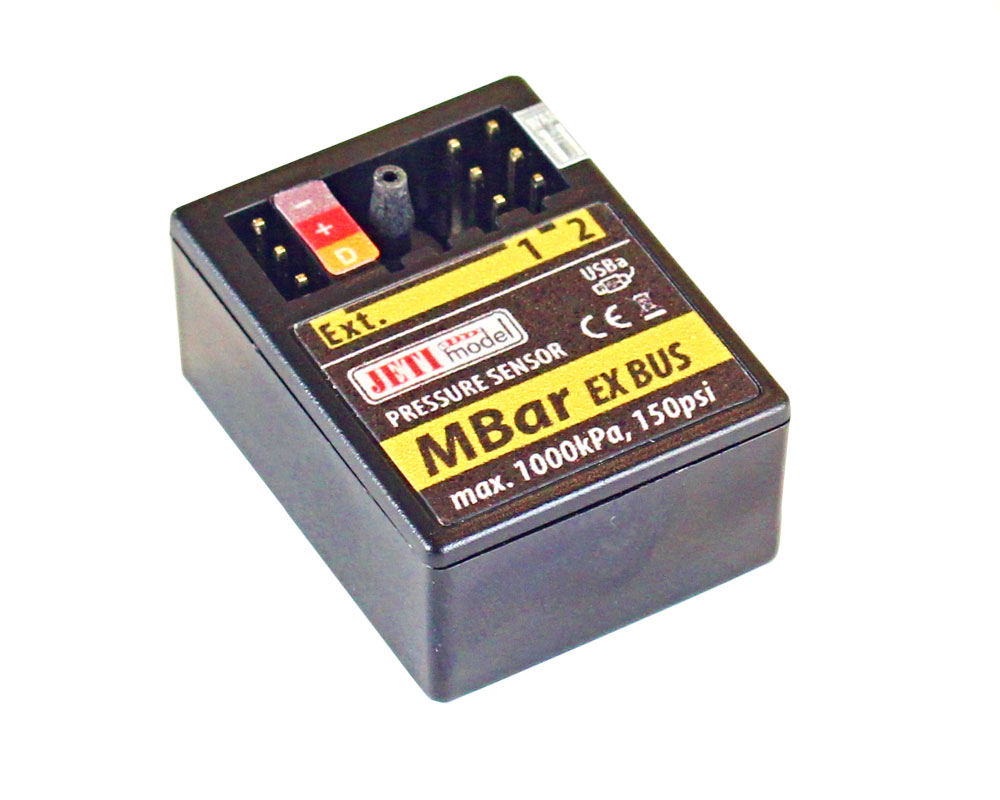
MBar – The MBar is an air pressure sensor. It will measure pressure of non-corrosive and non-ionized gases and liquids. The MBar sensor can be used for measuring pressure in containers with compressed air (retractable landing gear systems) or for controlling the oil pressure in hydraulic systems. Read more about the MBar EX Sensor here.
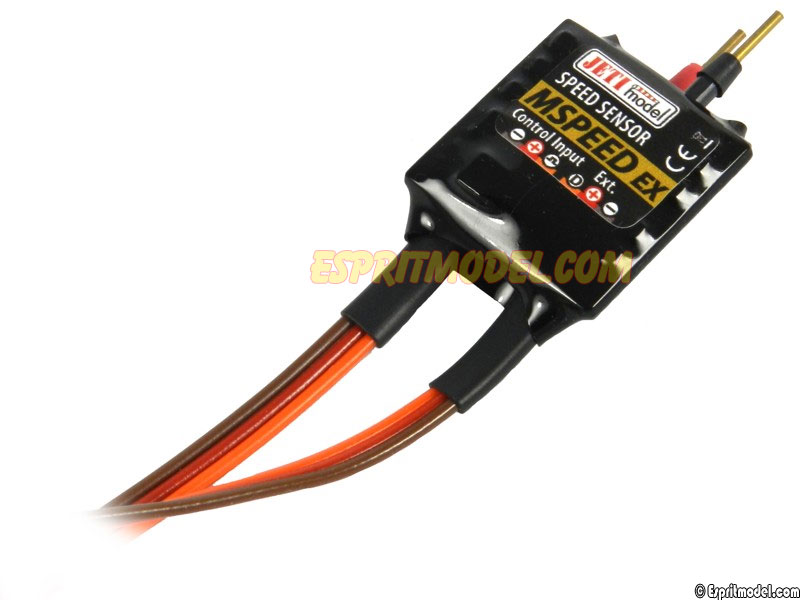
MSpeed and MSpeed 450 – Both of these sensors will give you the airspeed of your aircraft. They work using a pitot tube to measure the dynamic air pressure as you are in flight. The difference between the MSpeed and MSpeed 450 is simply the airspeed range that each will measure. The MSpeed450 is designed to be run in aircraft that fly at faster speeds, where as the MSpeed is designed for slower flying aircraft. Read more about the MSpeed here and the MSpeed 450 here.
MAlti – This sensor can provide calculated altitude above sea level, ambient fuselage air temperature, and air pressure data. These parameters are produced by measuring the atmospheric pressure. Since the MAlti is a very sensitive sensor, any slight change in altitude will result in a change in air pressure thus allowing calculation of how high above sea level your aircraft is. Read more here.
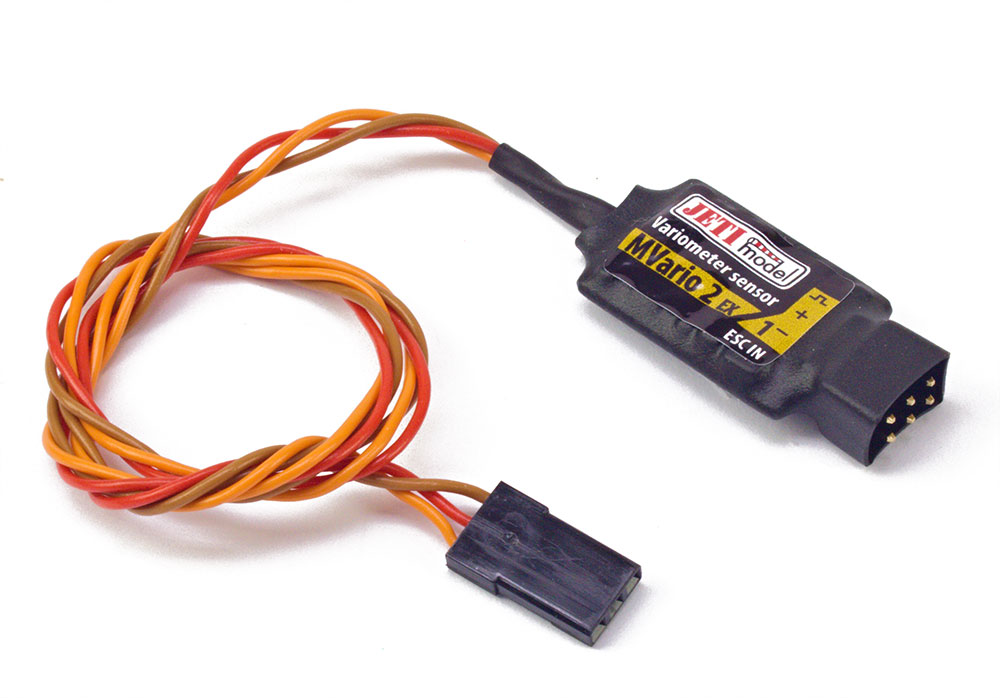
MVario2 – The Mvario2 is a system that measures atmospheric pressure and using the obtained data it calculates the altitude above sea level, airspeed, and the rate of climb as well as the rate of descent. Changes in climb and descent rates are signaled as well. The sensor also alerts you if any alarm setting is exceeded. The mvario2 will also work as an expander, allowing for connection of up to two additional sensors. Read more here.
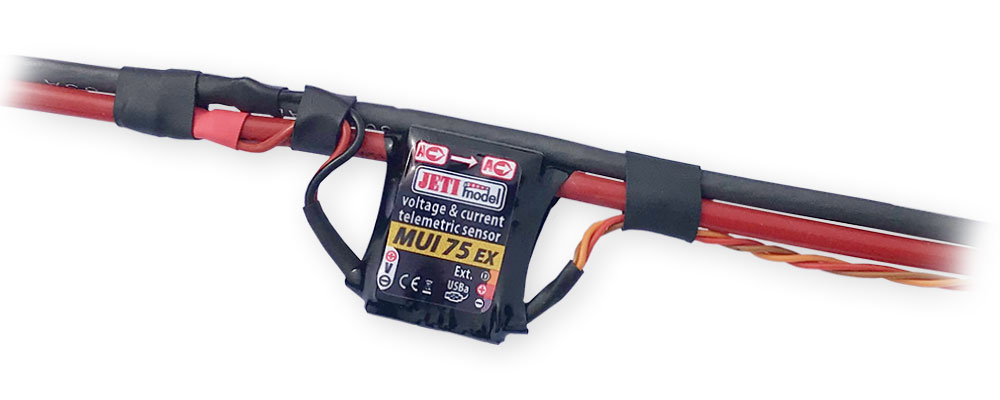
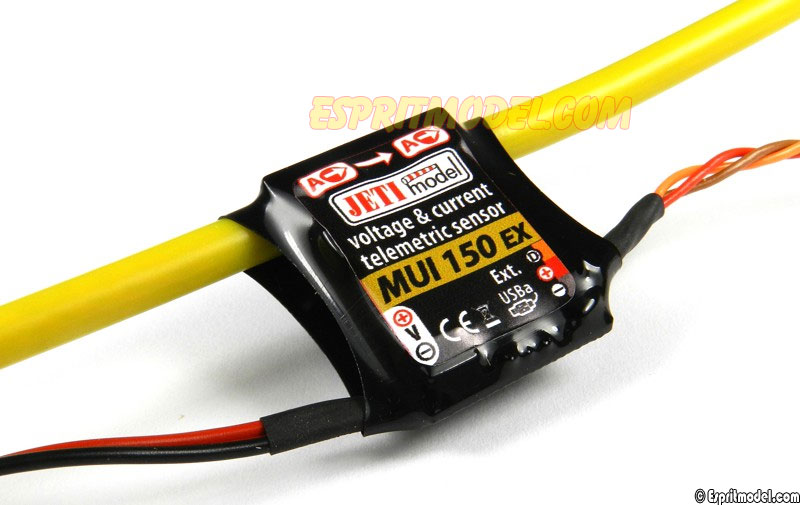
MUI – Our MUI sensors will measure voltage, current, and consumed battery capacity of your flight batteries. This sensor is available in five different amperage ranges, which are denoted by the number after the sensor. For example a MUI 30 will cover an amperage range of 0A to 30A, and a MUI 200 will cover a range of 0A to 200A. Find out more info here.
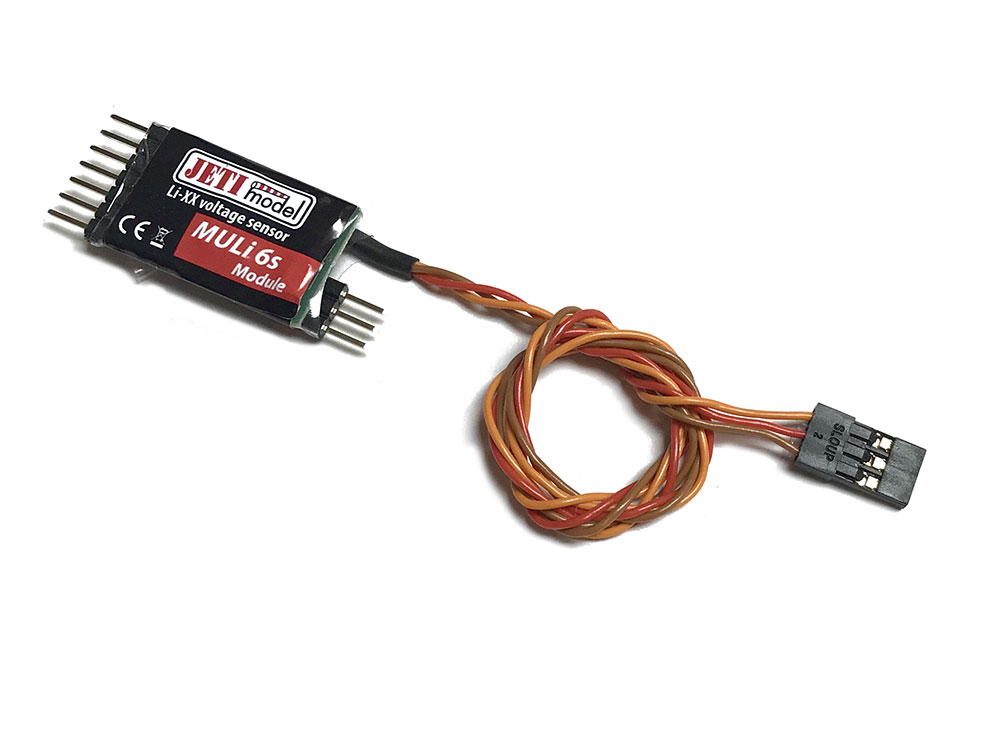
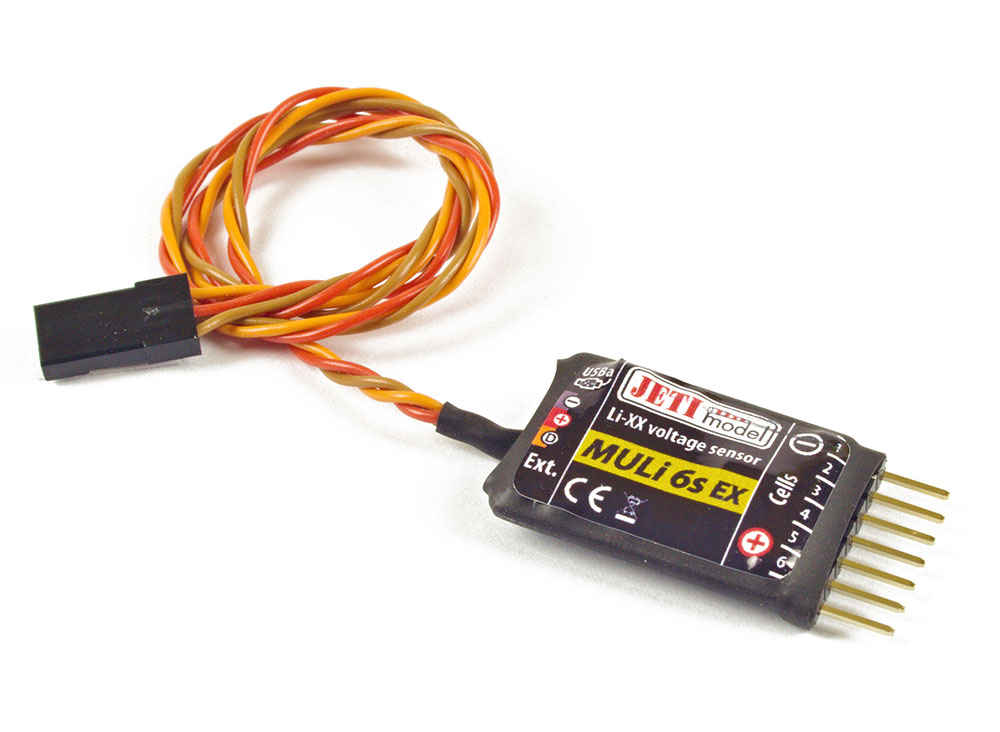
MULi 6s – The MULi 6s will measure the independent cell voltage (up to 6 cells) as well as total voltage of your lithium battery pack. Learn more here.
MULi 6s Module – The module version of the MULi 6s offers the same readings of independent cell voltage as well as total voltage of your lithium battery pack, but it is expandable by adding up to four additional modules. It can also be used as an expander for additional sensors. In addition to its expandability, the MULi 6s module offers cell voltage history and the difference between the strongest and the weakest cells. Read on about the sensor here.
MFlow2 – The MFlow2 is our second generation fuel flow sensor. It will measure the true fuel flow of gasoline or turbine jet fuel. We offer three different versions: G800, T800 and T3000. The G800 is for gasoline engines and will measure a flow rate of 20 to 800 ml/min. The T800 is for turbine engines with a flow rate of 20 to 800 ml/min and the T3000 is for turbine engines with a faster flow rate range of 50 to 3000 ml/min. Read more here.
MPGS – By using the Global Positioning Satellite system (GPS), the MGPS is able to pinpoint the exact location of your model. The MGPS can use that data to calculate the speed, altitude, the course azimuth, point of origin, and distance traveled of your model. Learn more here.
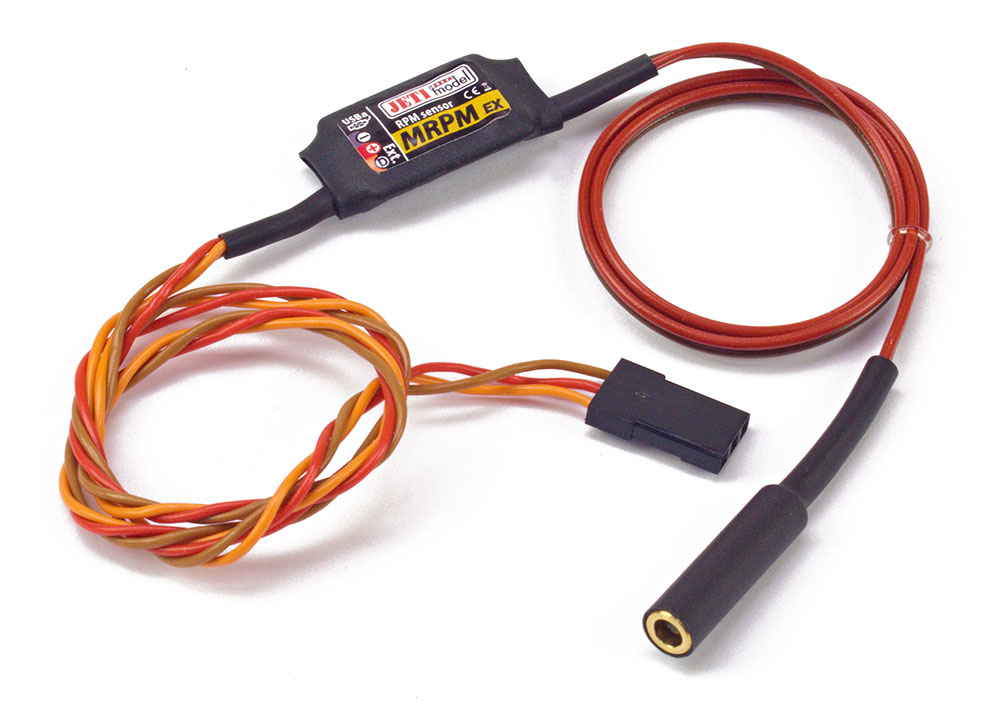
MRPM – The MRPM will measure the speed (Revolutions per minute, or RPM) of your models propeller optically. The optic sensor calculates RPM by monitoring the interruption of light (sunlight or incandescent light). Read more about this sensor on the page here.
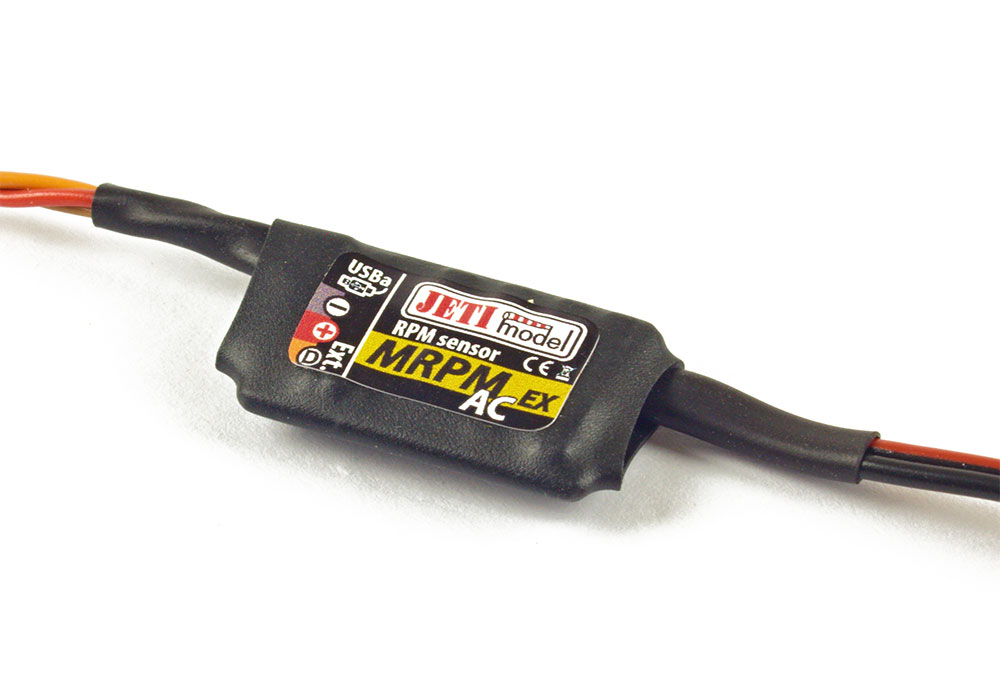
MRPM AC – The MRPM-AC will measure the speed (revolutions per minute, or RPM) of brushless motors through direct connection with two of the three motor wires (versus the previous Opto Sensor). Read more here.
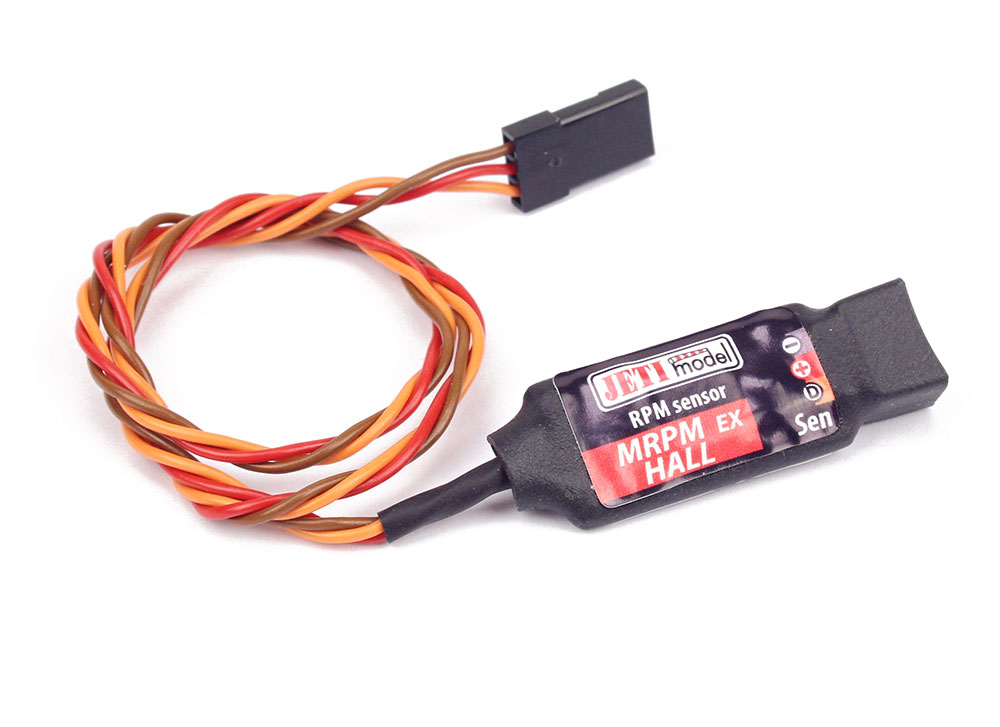
MRPM Hall – The MRPM Hall sensor provides RPM (revolutions per minute) and power level readings using magnetic Hall Effect and rare earth magnet. The MRPM HALL sensor measures the rotation speed and performance of the rotating surface. Read more here.
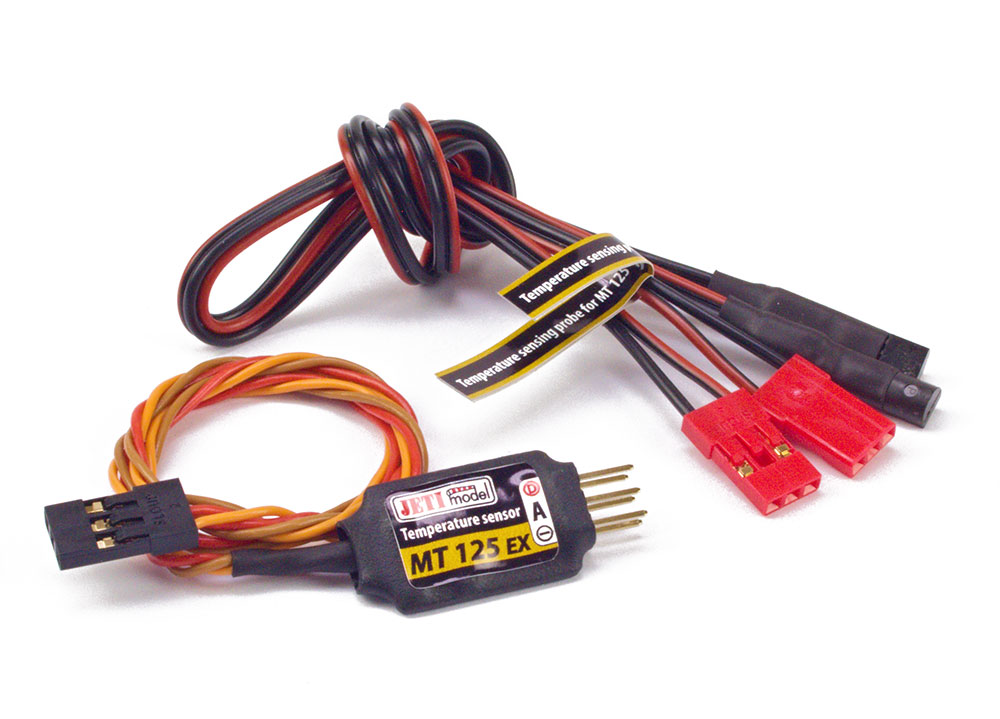
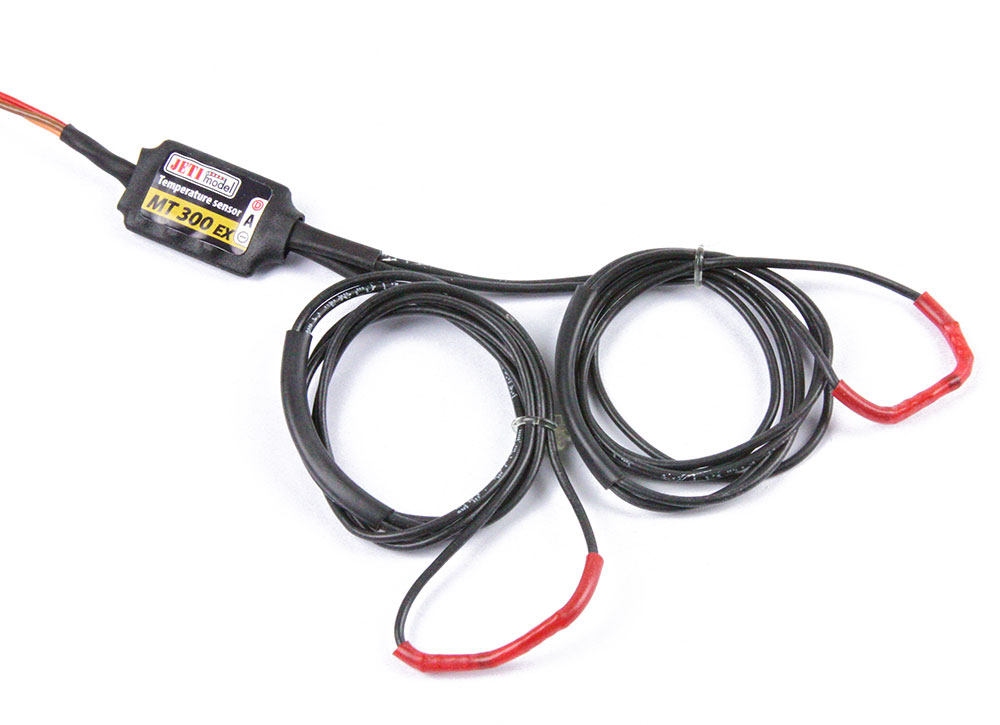
MT125 and MT300 – These sensors will monitor the temperature of whatever device you choose to place it around. It is, in simple terms, akin to a thermometer. The MT120 comes with two flat thermal probes, and the MT300 comes with two loop probes. Read about the MT125 here, and the MT300 here. Another difference between the two sensors is the range at which it will measure. The MT125 has a range of -55 to 125 degree Celsius, and the MT300 will operate at a range of -40 to 300 degree Celsius.
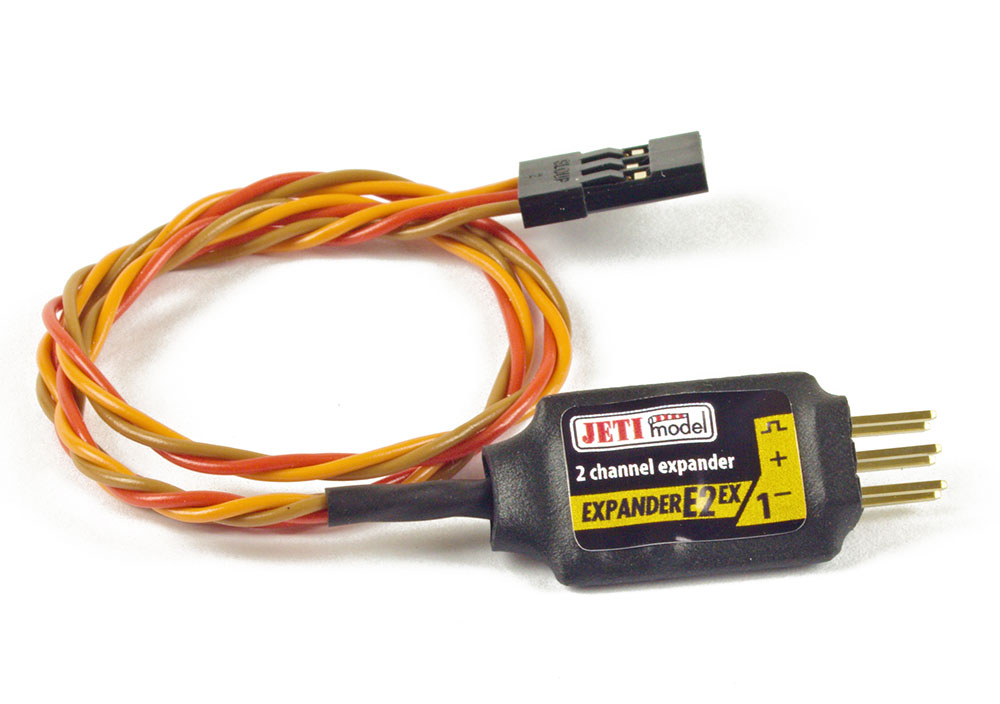
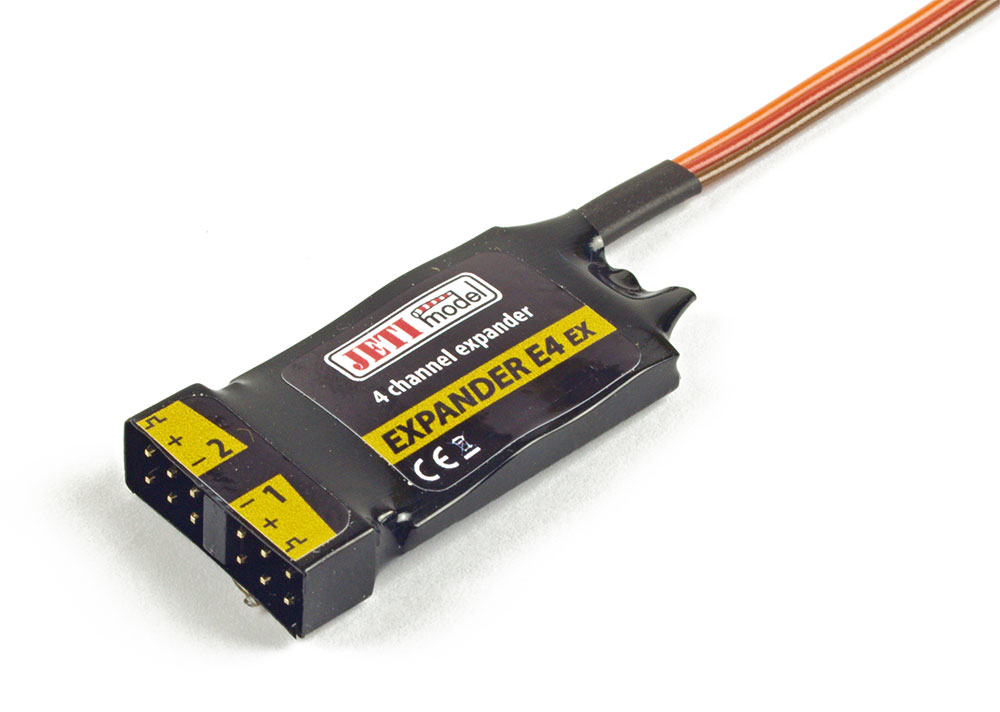
Expanders (E2, E4)– last but not least it is important to touch on the expanders. With so many sensors available, it is possible to run out of ports to connect them. The Jeti telemetry expander module allows you to increase the number of telemetry sensors in your aircraft. The E2 expander allows you to add up to two sensors and the E4 expander will allow for up to four sensors. Learn about the E2 here and the E4 here.